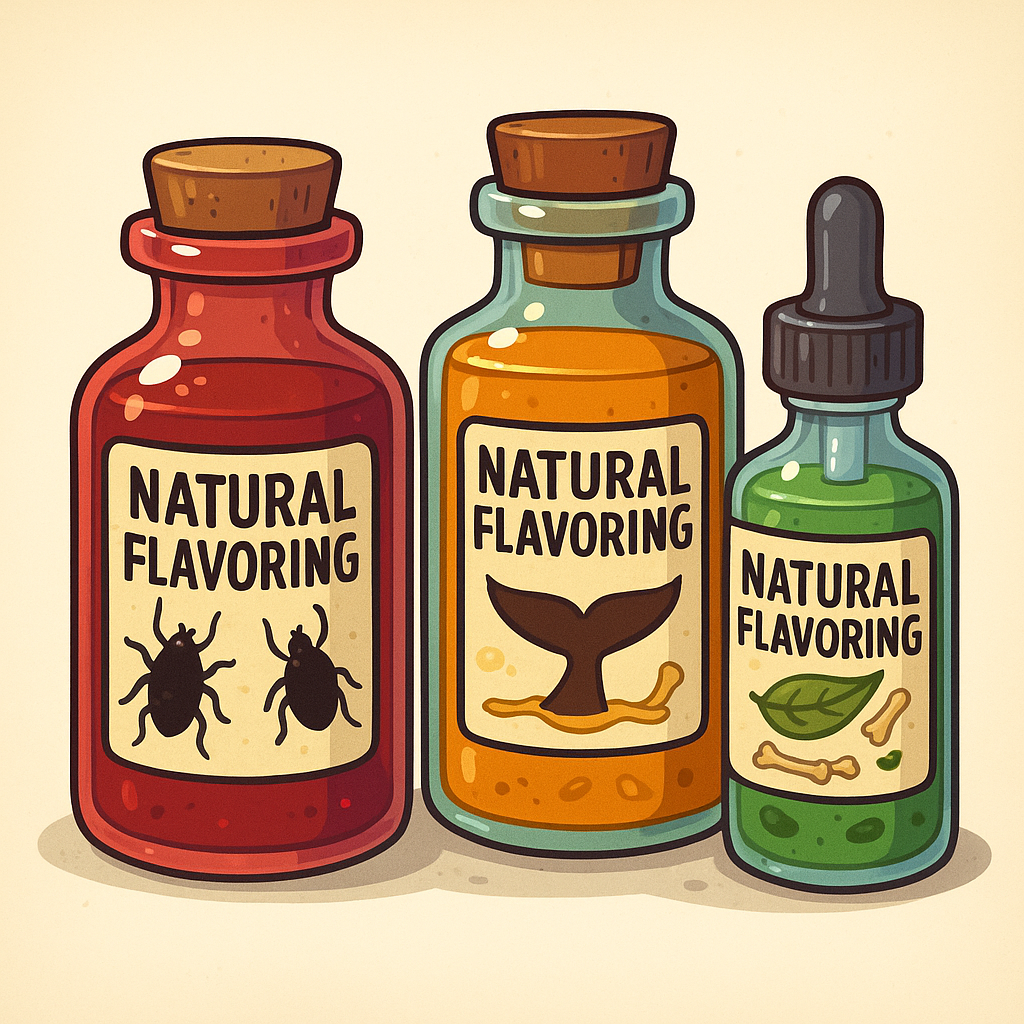
Ingredients & Additives — What “Natural Flavoring” May Be Hiding
Many ingredients are hidden by manufacturers through legal loopholes. “Natural flavoring” may simply mean a product tastes like the original source. “Artificial flavoring” often means it is not the way HKBH made it—hence, artificial. Grape juice used for flavoring or sweetening is often hidden inside a label’s “natural flavors.”
(Continued from last week)
Main Ideas
- “Natural flavors” can conceal animal-, dairy-, or grape-derived ingredients.
- Some additives are kosher and pareve (sometimes needing supervision), while others are not kosher.
- Always check ingredient sources and look for reliable kosher supervision on processed foods.
INGREDIENTS & ADDITIVES (many listed simply as “Natural Flavoring”)
- Acetic Acid — Source: plant juices, milk, oil, petroleum, sometimes muscles; final product of many aerobic fermentations. Status: when from petroleum, kosher, pareve (with supervision).
- Agar Agar — Source: seaweed. Use: substitute for gelatin (in creams and confectionery). Status: kosher, pareve.
- Albumin — Sources: blood (serum albumin), milk (dairy), eggs. Use: coagulant and stiffener in baked goods. Status: requires supervision.
- Alginate — Source: seaweed. Forms: calcium alginate, alginic acid, sodium alginate, propylene glycol alginate. Uses: thickener/stabilizer in pastry, jelly, ice cream, cheese, candy, yogurt, canned frosting, whipped cream, beer. Status: kosher, pareve.
- Alginic Acid — See: alginate.
- Alpha Amylase — Source: hog pancreas. Use: in flour (breaks down starches) and in medications. Status: not kosher.
- Alum (Aluminum Sulfate) — Source: earth; also called cake alum/patent alum. Use: clarifying oils and fats. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Ambergris — Source: whale intestine. Use: flavoring; also in perfume. Status: not kosher.
- Anise — Source: fruit of an herb (parsley family). Use: flavoring foods and beverages. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Argol — Source: sediment in wine casks during fermentation/storage. Use: manufacture of tartaric acid and malt vinegar. See also: cream of tartar; tartaric acid.
- Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) — Source: synthetic or corn. Use: nutrient. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Ascorbate Palmitate — Source: synthetic and palm oil. Use: preservative. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Benzoic Acid — Source: synthetic. Use: preservative. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole) — Source: synthetic. Use: antioxidant in cereals, stabilizers, shortenings, potato flakes/granules. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision when in corn oil).
- BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene) — Source: synthetic. Use: antioxidant in beverages, desserts, cereals, glazed fruits, dry drink mixes, potato flakes/granules. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision when in corn oil).
- Calcium Alginate — See: alginate.
- Calcium Carbonate — Source: limestone. Use: tooth powders; reduces wine acidity. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Calcium Chloride — Source: synthetic. Use: canned goods; preservative in cottage/cheddar cheeses. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Calcium Disodium (EDTA) — Source: synthetic. Use: flavor retention in canned soda/white potatoes; preservative in dressings, egg products, margarine, potato salad, lima beans, mushrooms, pecan pie filling, spreads. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Calcium Propionate — Source: synthetic. Use: preservative. Status: kosher; supervision preferred.
- Calcium Stearate — Source: compound of calcium and stearic acid (see Stearic Acid). Use: anti-caking in some spices (esp. garlic/onion salt); widely in tablets. Status: requires kosher supervision.
- Calcium Sorbate — Source: synthetic. Use: preservative. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Calcium Sterol Lactylate — Source: milk or soybeans. Use: instant mashed potatoes. Status: requires kosher supervision.
- Calcium Stearoyl Lactylate — Source: reaction of stearic acid and lactic acid. Use: dough conditioner; whipping agent; conditioner in dehydrated potatoes. Status: requires kosher supervision.
- Caprylic Acid — Sources: palm oil, coconut oil. Use: preservative and flavoring. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
- Carbon Black — Source: synthetic. Use: black coloring in confectionery. Status: requires kosher supervision.
- Carmine / Red 4 (Cochineal) — Source: insect (coccus cacti). Use: red coloring in apple sauce, fruit cocktail, jams, confections, baked goods, meats, spices. Status: not kosher.
- Carrageenan — Sources: seaweed and fresh moss. Use: emulsifier/stabilizer/thickener; substitute for gelatin. Status: kosher, pareve (no supervision).
Key Takeaway: “Natural flavors” aren’t always simple. Check sources and supervision—some additives are pareve and fine, while others (e.g., ambergris, carmine, hog-derived enzymes) are not kosher.